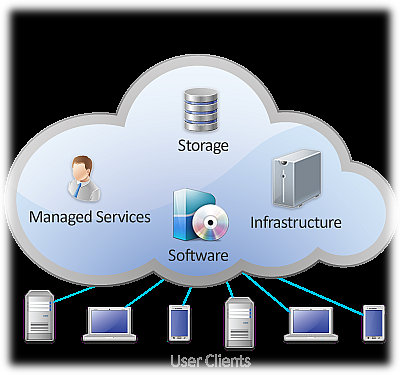
 The Cloud, also called cloud computing, is a radical change in the manner in which companies sell software, storage, processing power, and services, and in the manner in which consumers purchase those items. Amazon, Google, and other major corporations are pushing the cloud as the future of computing. Even Microsoft, the godfather of the traditional software model, has embraced the cloud to an increasingly great degree, offering cloud versions of many of its core offerings, including Microsoft Office 365 and Microsoft Dynamics CRM Online. The future and, increasingly, the present as well appear to belong in the Cloud. The Cloud, also called cloud computing, is a radical change in the manner in which companies sell software, storage, processing power, and services, and in the manner in which consumers purchase those items. Amazon, Google, and other major corporations are pushing the cloud as the future of computing. Even Microsoft, the godfather of the traditional software model, has embraced the cloud to an increasingly great degree, offering cloud versions of many of its core offerings, including Microsoft Office 365 and Microsoft Dynamics CRM Online. The future and, increasingly, the present as well appear to belong in the Cloud.
Cloud computing (whether software, hardware, or services) is delivered remotely over a network such as the Internet or a private intranet. Users consume the services on a device such as a desktop or mobile phone, using a purpose-built client application or a thin client (such as a standard web browser).
Other Types of CloudsWhen people use the terms “cloud” or “cloud Computing” they are typically referring to a public cloud, but clouds can be private or hybrid as well. A private cloud, also known as a dedicated environment, is set up by (or for) a single company for use by its personnel. Private cloud services can be delivered either through the Internet or through a private intranet. Hybrid clouds combine elements of both clouds together, delivering some services through the Internet and others through a dedicated intranet that does not rely on Internet connectivity.
Benefits of Cloud Deployments
Cloud deployments provide several benefits over traditional on-premises deployments.
- More secure – A widespread perception exists that the cloud is less secure than on-premises deployments. However, the reality is that cloud security (PDF) trumps on-premises security, facing a more limited variety of attacks, a smaller number of incidents, and fewer total breaches than on-premises deployments.
- Less expensive up front – Because there is no equipment or licenses to buy, cloud deployments cost less to set up.
- Frequently cheaper long term – Cloud deployments are frequently, but certainly not always, cheaper over the long term as well. For smaller companies that do not have their own data centers and system administrators already, cloud deployments can actually cost less over time. Companies that already have those facilities and staffs in place will likely find that on-premises systems with traditional perpetual licenses are less expensive long-term.
- Consistent IT costs – Service providers deliver cloud services at a consistent monthly rate, making it easier to budget reliably for IT costs. There are no surprise costs for equipment failures or upgrades.
- Quicker to deploy – Sign up, download the client application, and you are ready to go. The cloud eliminates virtually all the set up and configuration.
- Simpler to maintain – Service providers perform all of the necessary maintenance on the server end of the client-server relationship.
- Automatic upgrades and updates – Service providers maintain all of the servers and performs all of the software updates.
- Immediate access to cutting-edge software – With SaaS, you always have access to the most recent releases and updates from the software publisher.
- Gain access to infrastructure and expertise – Few companies can afford the equipment and personnel necessary to run a reliable data center. The cloud allows smaller companies to leverage the expertise and equipment of larger companies that are focused on delivering services remotely.
- Uptime guarantees – Most cloud service providers guarantee 99.9% uptime.
- Less risk – Adopting new technologies and software versions involves risk. Cloud service providers assume nearly all of that risk.
- Easy to add or decrease capacity at will. With cloud deployments, it is much easier to increase and decrease capacity.
- Focus on your core business – Choosing cloud services—whether SaaS, STaaS, Managed Services, or some other offering—allows you to reallocate resources from IT to the core business that actually makes you money.
Disadvantages of Cloud Deployments:
Although there are several strong benefits of using the cloud deployment model, there are a few drawbacks as well.
- Higher long-term cost - The long-term cost of cloud services is generally higher than the cost of owning perpetual licenses (assuming you do not continually upgrade your perpetual-licensed software).
- Less control – When you own your own hardware or software, you can set it up and administer it how you please. With Cloud deployments, you consume a service that is typically more standardized.
- Less customizability - Cloud applications are often not customizable to the same extent as on-premises deployments are.
- Regulatory restrictions - Regulations in some industries and circumstances restrict the use of Cloud deployments, requiring physical control and/or strict segregation of data.
- Difficult integration - It is often more difficult to integrate legacy systems or custom line-of-business applications.
|